Which Equation Offers the Most Precise Description of Accounting Practices?
According to the accounting equation, the sum of a company's liabilities and the amount of equity held by its shareholders is equivalent to the total assets of the company. This means that the entire assets of a business are identical to this figure. It makes no difference how large the organisation is, this is always the case.
The direct connection that exists between the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company is regarded as the system's foundation when it comes to double-entry accounting because this relationship is considered to be the basis of the system. The accounting equation is used in double-entry accounting, which explains why this is the case. Accounting is based on a mathematical formula, which ensures that the balance sheet's objectivity will not shift throughout the course of time. That is to say, for each and every entry that is made on the debit side of the ledger, there is an entry (or coverage) that corresponds to it that is made on the credit side of the ledger. This can also be stated as the following:
The accounting equation is known by a number of names, including the fundamental accounting equation and the balance sheet equation, to name just a couple of the many titles that have been used to refer to it.
So what does a full Balance Sheet look like?
— Michael Siaw Larbi (@_iamMSL) July 8, 2022
Here is everything covered so far in one full picture
If you look carefully, it lists all Assets and lumps all Liabilities and Equity together in this format
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This is the famous Accounting Equation pic.twitter.com/gauyHQadoN
KEY TAKEAWAYS
It is generally agreed upon that the accounting equation serves as the fundamental conceptual foundation that underpins the double-entry accounting system. [Citation needed] [Further citation is required] [Further citation is required] [Further citation is required]
According to the accounting equation, the total shareholders' equity in a company should be equal to the sum of the company's liabilities as well as the total value of the company's assets. This should ensure that the accounting equation is followed correctly. This information ought to be reflected in an accurate manner on the balance sheet of the organisation.
In this discussion, the valuable resources that are under the authority of the corporation and are referred to as its assets are what are meant by the phrase "assets." The magnitude of the obligations they are responsible for meeting is a direct reflection of their responsibilities.
The financing of an organization's assets consists of two components: its liabilities and the equity that its shareholders have invested in the company. This component can be further subdivided into a few other subcategories if necessary.
When a corporation chooses to fund its capital expenditures through the issuance of shares of stock rather than through the use of debt in order to finance such expenditures, the money that is raised is counted as an addition to the equity of the firm's shareholders.
It Is Absolutely Necessary to Have a Solid Understanding of the Accounting Equation
Regardless of the size of the company, the assets and liabilities that are reflected on the balance sheet of the organisation are the fundamental components that define the company's overall financial health. These components are represented on the balance sheet. The third section of the balance sheet is referred to as equity, which may also be referred to as owners' equity or shareholders' equity. This section may also be referred to as the equity section depending on the context.
The accounting equation is a representation of how these three key components are connected to one another and how that connection may be comprehended. The accounting equation depicts the relationship that exists between these three significant components. In addition to this, it demonstrates how the relationship may be comprehended in terms of the various ways in which it can be portrayed.
The valuable resources that are under the control of the company are referred to as the firm's assets. On the other hand, the obligations that are the responsibility of the company are referred to as the company's liabilities. The financing of an organization's assets consists of two components: its liabilities and the equity that its shareholders have invested in the company. This component can be further subdivided into a few other subcategories if necessary. If it is financed through the issuance of debt, then it will be reflected as a liability on the balance sheet; however, if it is financed through the sale of equity shares to investors, then it will be reflected as an increase in shareholders' equity. If the transaction is financed through the sale of equity shares to investors, then it will be reflected as an increase in shareholders' equity. If it is financed by the sale of equity shares to investors, then it will be shown as an increase in shareholders' equity if and only if it is financed in this manner.
The accounting equation is a useful tool that can be used to determine whether or not the books and accounts of the company provide a picture of the numerous business operations that are carried out by the organisation that is accurate. This may be accomplished by using the accounting equation. The following is a list of some instances of the many categories of items that are included on the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, and net worth.
Anything of worth that can be exchanged for cash or utilised in its stead is referred to as a "asset," and the term is used to describe such things. This consists of cash as well as various forms of money equivalents. In addition to Treasury bills and certificates of deposit, another sort of asset that might be considered an example of a liquid asset is mutual funds.
The sums of money that customers owe to the firm as a result of the sale of the company's products are itemised and broken down into their component parts in the accounts receivable section of the books. These sums of money result from the sale of the company's products. In addition, in the perspective of the law, inventory is regarded as an asset.
The assets that are most valuable to an organisation are almost always the ones that have the highest total value as well. These include the vehicles, structures, and other pieces of real estate that are a part of the corporation. These are some examples of fixed assets, which are often kept for a considerable amount of time—sometimes even decades—before being sold or otherwise disposed of.
A company's list of liabilities will always include all of the tasks it must fulfil and the expenditures it is responsible for paying. These payments are required to ensure that the business will be able to continue operating normally in the future.
A debt, regardless matter whether it is a loan with a protracted payback schedule or a bill that has been past due on its payment, is termed a liability.
The entire cost takes into account not just dividends, salaries, and other kinds of payment, but also the amount spent in rent, taxes, and utility bills.
Equity Holdings of the Company's Shareholders
Start by deducting the total liabilities from the total assets of the company in order to get the amount of equity that is held by the company's shareholders. This will give you the total amount that represents the equity in the company held by the shareholders.
It is feasible to describe it as the total amount of money that would be left over after a company has paid off all of its obligations and sold all of its assets if the company were to immediately cease operations. This is the amount of money that would be left over after the company has paid off all of its obligations and sold all of its assets. This is the sum of money that constitutes what is referred to as the "net worth" of the company. After that point, money would be given out to the stockholders in the form of dividends as a form of distribution.
Earnings that are not distributed to shareholders and are, as a result, retained by the company are referred to as retained earnings. This number represents the total amount of profits that were kept by the company rather than being distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. This decision was made in order to maximise shareholder value.
Think of retained earnings as savings because it reflects the total profits that have been saved and put aside (or "retained") for future use. You can think of retained earnings as saves because it reflects the total profits. Because it reflects the company's overall income, retained earnings can be thought of as a form of savings. Because they are a representation of the complete profits that the business has made, retained earnings can be thought of as savings.
Performing Calculations Using Accounting Equations and Formulas, in Addition to Working with Them
The value of an asset can be calculated by adding the value of its obligations to any equity that is held by the owners.
When calculating the financial health of a company, the Assets must always equal the Liabilities plus the Owner's Equity.
On the balance sheet, you will discover the following components, each of which plays a part in the accounting equation: assets, liabilities, and equity. Those components are listed in the following order: assets, liabilities, and equity.
Find out how much the total assets of the company are that are recorded on the balance sheet for the time period that is pertinent to the inquiry.
Determine the aggregate value of all of the company's liabilities, which must then be recorded in a distinct part of the balance sheet.
Determine the whole amount of the shareholder's equity in the company, then add that amount to the total amount of the company's liabilities to get the total amount of the company's equity.
The total amount of the company's liabilities, in addition to the amount of equity held by all of its stockholders, will equal the value of the company's entire asset portfolio.
Take, for instance, the report that the company that holds the dominating market share in the retail industry, XYZ Corporation, made on its balance sheet for the most recent complete fiscal year. The following is how the report is formatted:
There is a total asset value of 170 billion dollars spread across all of the assets.
Total liabilities: $120 billion
Shareholders collectively own a total stock value of $50 billion in their companies.
If we answer the question on the right-hand side of the accounting equation, which is equity plus liabilities, we have the result of ($50 billion plus $120 billion), which is equivalent to $170 billion. When we calculate the equation using the left-hand side, which is assets minus liabilities, we get the same result as when we solve the problem using the right-hand side. This number is comparable to what the company reports in its financial statements as the value of its assets, thus it is the same thing.
Regarding the Double-Entry Process
An intricate, detailed, and multi-item presentation of a balance sheet is capable of being condensed into an expression that is known as the accounting equation.
The viewpoint that this representation holds, in its most basic form, is that all uses of capital (assets) and all sources of capital are equivalent to one another. This is the most fundamental form of the representation. This suggests that equity capital ultimately results in the equity of owners, but borrowed capital ultimately results in liabilities for the company.
Every single business transaction will have a record in at least two of the company's accounts if the books are being kept in the acceptable manner by the company. If a corporation, for instance, obtains financing from a financial institution in the form of a loan, the borrowed funds will be reflected in the company's balance sheet as an increase in both the company's assets and its loan debt. This is because an increase in assets means an increase in the value of assets, while an increase in loan debt means an increase in the value of loan debt. This is due to the fact that the corporation will now owe a greater sum of money on its loans as a result of the additional monies that were borrowed.
When a company purchases raw materials and pays for them in cash, this will result in an increase in the company's inventory (which is an asset), but it will also result in a reduction in the cash capital that is accessible to the company at that moment. When a company buys raw materials and pays for them in cash, this will lead to an increase in the company's inventory (which is an asset) (another asset). Accounting is referred to as double-entry when there are two or more accounts that are affected by each transaction that is carried out by a firm. This type of accounting is the one that is utilised when most businesses keep their books. This method of keeping financial records is by far the most typical one. As a consequence of this, it is guaranteed that it is able to put together accurate financial accounts.
Because it verifies both sides of the equation, the use of two entries in accounting ensures that the accounting equation will never become unbalanced. This is because of the nature of accounting. As a consequence of this, one can draw the conclusion that the value that appears on the left side of the equation will invariably correspond to the value that appears on the right side of the equation.
To put this another way, the total amount of all of the company's liabilities, in addition to the amount of equity that is held by the shareholders, will always be equal to the value of the firm's total assets, regardless of how you choose to express it.
As a direct result of the widespread usage of the double-entry accounting system, the processes for recording financial transactions and creating statistics have grown more standardised and less prone to error. This is because the system uses two sets of books to record each transaction.
The accounting equation ensures that all entries in the books and records are checked, and that there is a relationship that can be verified between each item of liability (or expense) and its corresponding source, or between each item of income (or asset) and its source. Additionally, the accounting equation ensures that there is a relationship that can be verified between each item of income (or asset) and its source. In addition, the accounting equation assures that there is a relationship between each item of income (or asset) and its source, which can be validated by using the accounting equation. This equation is also responsible for the completion of the books and records, which can be linked to the fact that it was used.
The Equation's Provisions, Both in Terms of Opportunities and Restrictions
Even if a corporation is showing profits on its balance sheet, accounting equations are unable to convey to investors how well the company is actually doing, despite the fact that those earnings are being displayed on the sheet. Investors are responsible for analysing the data and arriving at their own conclusions regarding whether the company has an insufficient amount of assets, an excessive number of assets, or an excessive amount of liabilities, or whether its financing is adequate to ensure the company's continued growth over the long term. This analysis and these conclusions are the responsibility of the investors. The duty for conducting this investigation and arriving at these findings is with the investors.
An Example Taken From Real Life
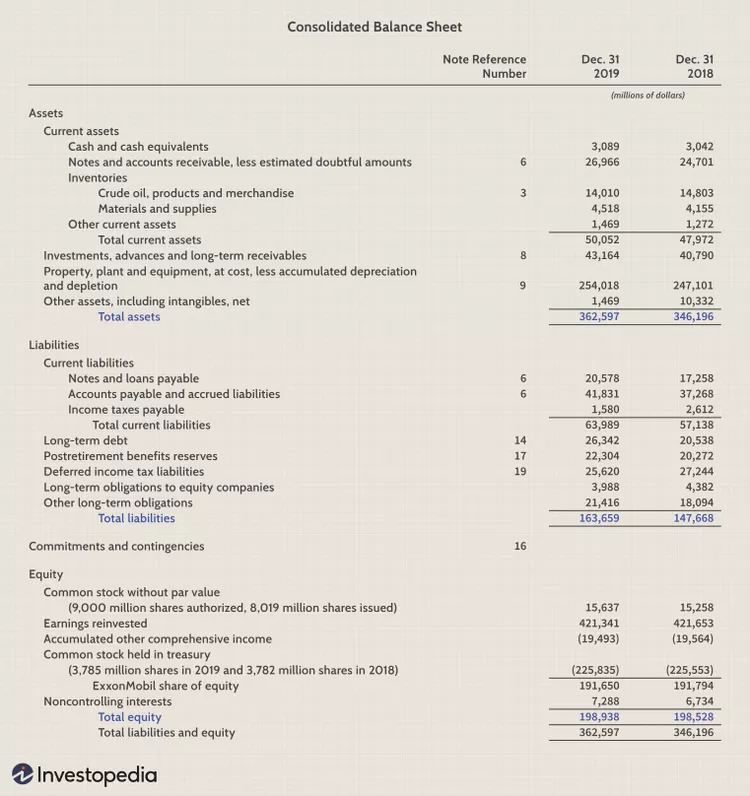
The following is a portion of the balance sheet for Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM) as of the 31st of December, 2019, expressed in millions of dollars:
The sum of all of the assets came to a total worth of 362 597 US dollars.
To fulfil all of the obligations that had been made would cost a total of 163,659 dollars.
The total value of the equity came to 198 938 dollars when everything was added together.
If you want to be correct in your calculations, the accounting equation can be calculated as follows:
The following equation can be used to determine an organization's total obligations to its creditors: The whole amount of obligations is equal to $163,659, and the equity equals $198,938, thus the total amount is equal to $362,597. (which is analogous to the total value of all assets owned throughout the period)
When it comes to doing accounting duties, why is it very necessary to have an equation?
A succinct explanation of the relationship that exists between the asset, liability, and equity parts of a balance sheet can be found in the form of an equation that is used in accounting. A balance sheet is constructed using these individual parts. If there is no change in any of the other features of a firm, then the equity of the company will grow in direct proportion to the increase of its assets, and vice versa. This is the case even if there is no change in any of the other aspects of the company. When liabilities decrease, such as when debt is paid off, equity increases; nevertheless, equity decreases when responsibilities increase, such as when more debt is taken on. One example of this scenario is when a debt is paid off. A drop in equity will occur if there is an increase in responsibilities, such as when additional debt is paid off. These fundamental ideas are an unavoidable prerequisite for the various procedures that are engaged in contemporary accounting.
What are the three components that make up the equation that is used in accounting?
The accounting equation can be decomposed into three parts: the assets, the liabilities, and the equity that is held by the shareholders of the company. The formula can be derived with relative ease, and it is presented in the following form: The total assets of a company are equivalent to the sum of the firm's liabilities plus the amount of equity held by the shareholders of the company. The double-entry accounting method, which is becoming increasingly common in many parts of the world, was developed with the intention of providing an accurate depiction of all of a company's assets.
In the context of the accounting equation, what does it precisely mean to say that one possesses an asset?
What characterises an asset for a corporation is the company's ownership over something with economic value that can be used to the company's advantage either now or in the future. An asset can be used to benefit the firm either now or in the future. The value of an asset can be maximised for the organisation in either the present or the future. By making use of an asset, a benefit to the company can be obtained either immediately or at some point in the not-too-distant future. They are made up of things that are immobile, such as buildings and pieces of machinery, and cannot be moved independently. Possibly included in this category are financial assets such as stock and bond investments, as well as possibly even other forms of financial assets. There is also the possibility that these assets are intangible, like patents, trademarks, or goodwill. This is another possibility. This is yet another option to consider.
When it comes to the accounting equation, what does it mean to have anything that is considered a liability?
A corporation's list of liabilities will include every single debt that it has accrued during the course of its history, so long as the company continues to operate. To give just a few instances, the various forms of liabilities include items like loans, accounts payable, mortgages, delayed revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses.
When it comes to the topic of accounting, what does it precisely mean when it refers to shareholders' equity in an equation?
The total value of the company, expressed in terms of dollars and referred to as the shareholders' equity is what is meant when people talk about the value of the company. To put it another way, it is the total amount of money that would be available for distribution if the company were to completely sell off all of its assets and pay off all of its debts. In other words, it is the amount of money that would be left over after paying off all of the debts. The amount that has not yet been paid is considered to be the shareholders' equity, and it will be restored to the shareholders who own the company.
